OIDC (OpenID Connect) binding
OpenID is an easy and safe way for people to reuse an existing account and user profile from an identity provider. OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an interoperable authentication protocol based on the OAuth 2.0 framework of specifications.
 Example
Apple, Google, or Microsoft can sign-in to any OpenID-enabled application or website without
creating a new registration and password.
Example
Apple, Google, or Microsoft can sign-in to any OpenID-enabled application or website without
creating a new registration and password.
How OIDC Works
The OpenID Connect protocol, in abstract, follows these steps:
- End user navigates to a website or web application via a browser.
- End user clicks sign-in and types their username and password.
- The RP (Client) sends a request to the OpenID Provider (OP).
- The OP authenticates the user and obtains authorization.
- The OP responds with an identity token and usually an access token.
- The RP can send a request with the access token to the User device.
- The UserInfo Endpoint returns claims about the End-User.
octoplant and OIDC
See the FAQ for more information about OIDC with octoplant.
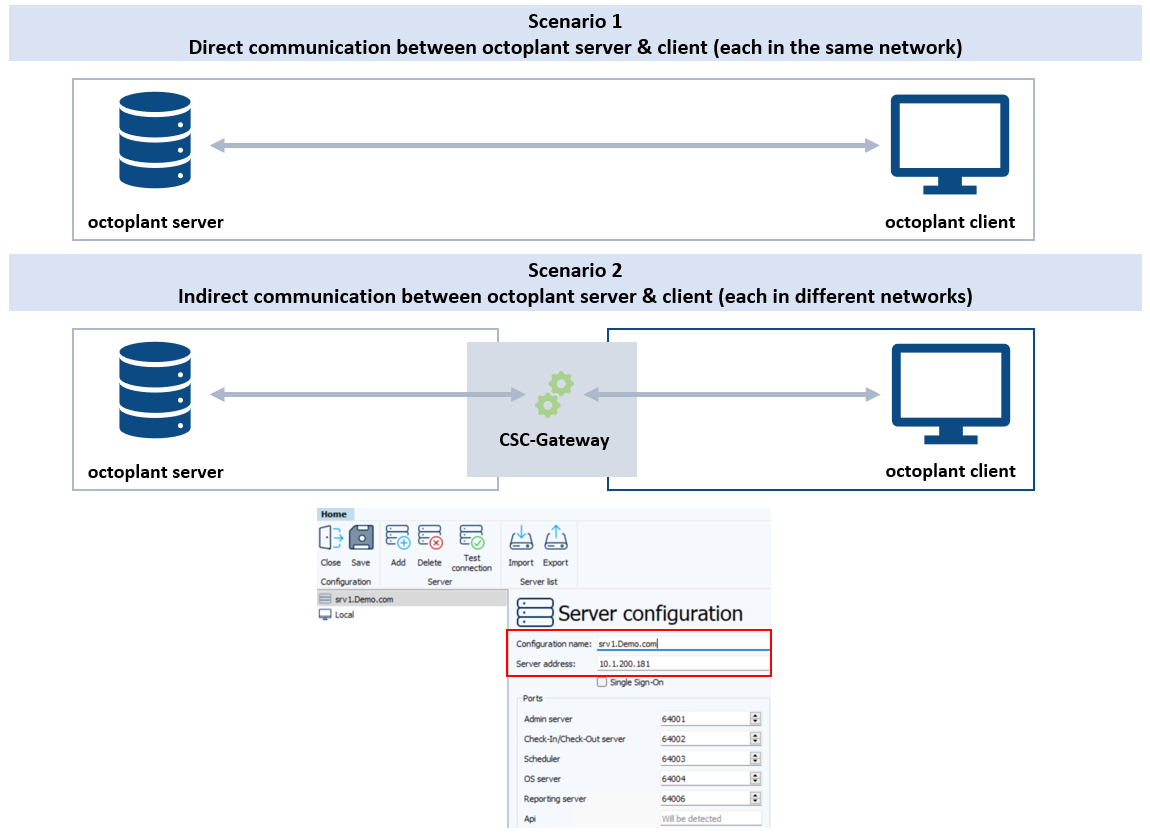
octoplant without OAuth
Configuration without external token handling and ID provider:
-
octoplant server and client can communicate via IP address or computer name (FQDN1)
-
No additional handling of external certificates or tokens is required
-
If a CSC Gateway is required (for example, using separated networks), this could be configured without additional external effort
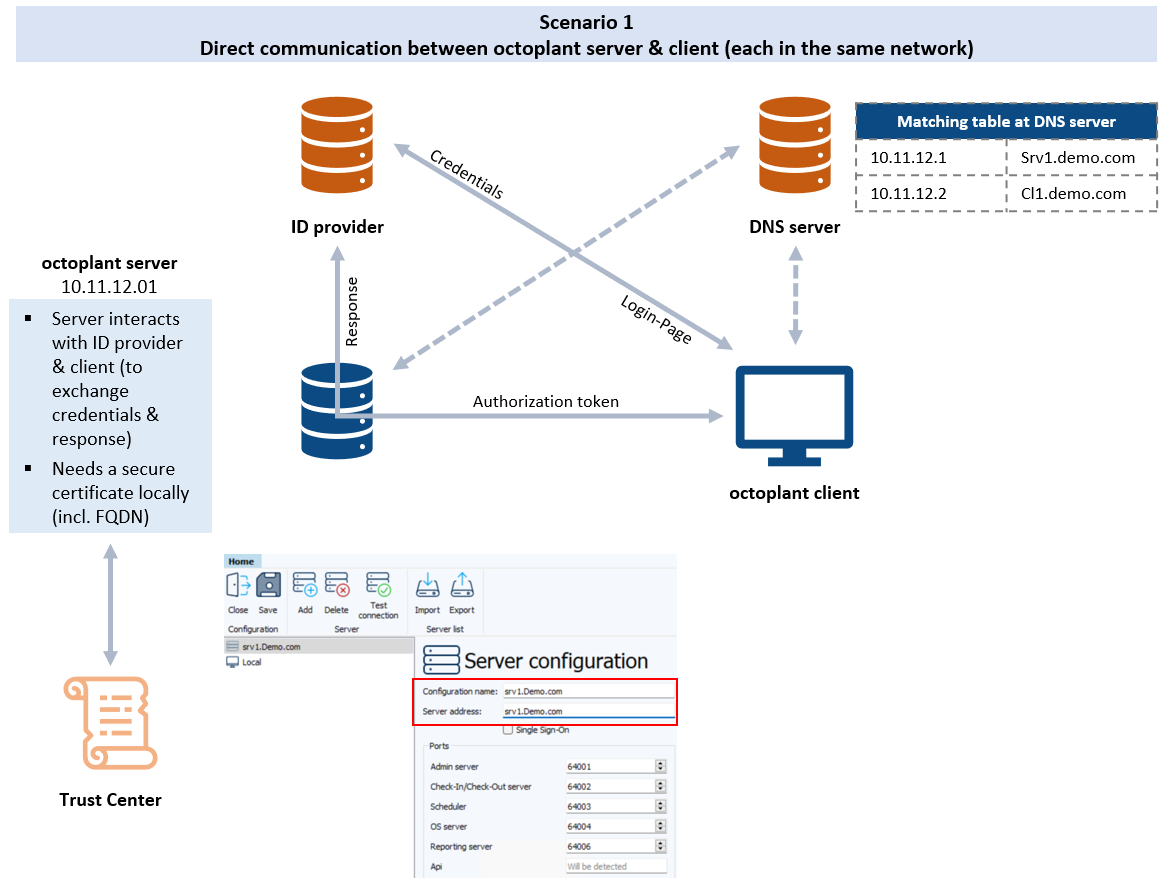
octoplant with OAuth
Integration of ID provider including token handling:
-
octoplant server and client can only communicate with their FQDN
-
This is required, because the FQDN from the server system is included in the certificate or token which is required for OAuth
-
Key changes when using OAuth:
-
Generation and implementation of certificate on octoplant server
-
Communication to DNS server is required
 DNS servers are normally configured for octoplant automatically by the octoplant server operating system.
See your IT team for configuration details.
DNS servers are normally configured for octoplant automatically by the octoplant server operating system.
See your IT team for configuration details. -
Connection to ID provider required
-
May also require update of login configuration on client system
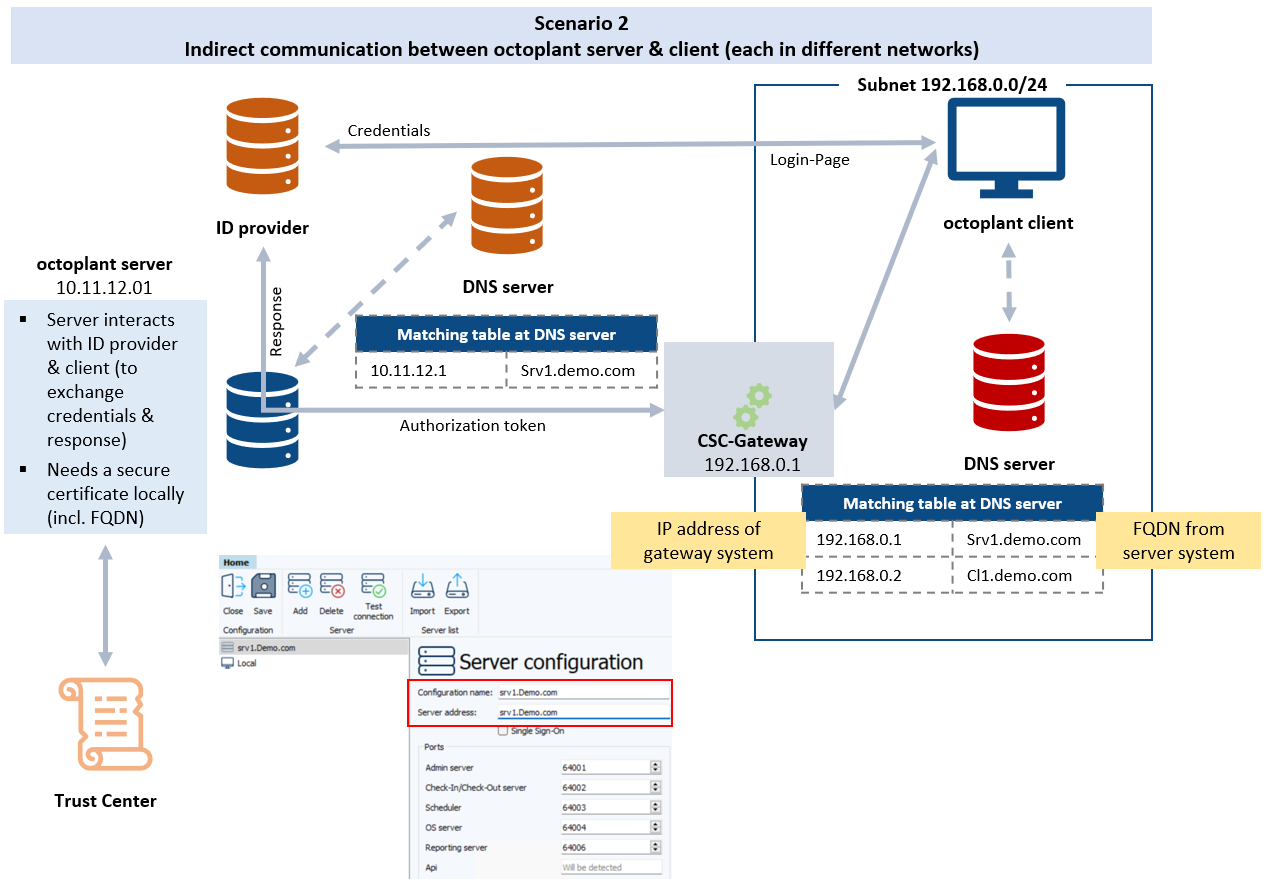
-
octoplant with OAuth and CSC-Gateway
Integration of ID provider including token handling:
-
octoplant server and client can only communicate with their FQDN
-
This is required, because the FQDN from the server system is included in the certificate or token which is required for OAuth
-
Key changes when using OAuth and separated networks:
-
Generation and implementation of certificate at octoplant server
-
Communication to global DNS server is required
-
Connection to ID provider required
-
May also require update of login configuration at client system
-
Additional DNS server in separated network and adjustment of matching table required
 DNS servers are normally configured for octoplant automatically by the octoplant server operating system.
See your IT team for configuration details.
DNS servers are normally configured for octoplant automatically by the octoplant server operating system.
See your IT team for configuration details.
-
ID providers for use with octoplant
The following is a list of ID providers linked to instructions on how to implement in octoplant:
OIDC terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| access token | In the OAuth 2.0 specification, an access token is an opaque key that allows a Relying Party (RP) client to access things on a resource server. In Connect, access tokens are JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) that enable access to the Connect's OIDC-based /userinfo endpoint and, depending on the scopes granted, potentially to other Connect APIs as well. They also represent the fact that a user has logged in to your application. |
| authorization code | In the Authorization Code Grant flow, this is a one-time code that can be redeemed at Connect's token endpoint for OAuth 2.0 or OIDC tokens (for example, access token, refresh token , ID token). |
| authorization endpoint | The HTTP endpoint used to initiate OAuth2.0 or OIDC grant flows. For Connect, this is /oidc/authorize. |
| authorization server | OAuth 2.0 name for the entity that grants tokens to clients on behalf of a resource owner. Connect is an authorization server when a registered RP client uses it to obtain tokens. Equivalent to an issuer in OIDC terminology. |
| claim | A piece of information about a user such as their email address. An RP client requests a set number of user claims from Connect by specifying the corresponding scopes in its initial request. |
| client | OAuth 2.0 name for the part of your application which will request and use OAuth 2.0 tokens. Equivalent to Relying Party (RP) in OIDC terminology. |
| grant flow | A particular sequence of interactions, initiated by an RP client, that ultimately ends with the granting of tokens. OAuth 2.0, OIDC, and their extension specifications, collectively define several different possible grant flows. |
| ID Token | In the OIDC standard, a JWT issued by the authorization server (or issuer) asserting certain information (claims) about an end user. |
| issuer | The entity that issues a JWT, such as Connect in the case of an ID Token. Equivalent to an authorization server in the original OAuth 2.0 standard. |
| OAuth 2.0 | Authorization protocol built around access and refresh tokens that enable the transfer of resources between systems. |
| OpenID Connect (OIDC) | Authentication layer built on top of OAuth 2.0. OIDC extends the OAuth 2.0 protocol to standardize user authentication and access to user information between systems. OpenID Connect enables an Internet identity ecosystem through easy integration and support, security and privacy-preserving configuration, interoperability, wide support of clients and devices, and enabling any entity to be an OpenID Provider (OP). |
| OpenID Provider (OP) | Provides authentication of the user and authorizes the RP with an ID token and usually an access token. |
| protected resource | In OAuth 2.0, any endpoint or resource that requires authorization (such as an access token) to access. |
| relying party (RP) | OIDC name for the OAuth 2.0 client. |
| resource owner | OAuth 2.0 name for the user, the entity (person) who owns the resource, where the resource in question is their ability to authorize access. |
| resource server | OAuth 2.0 name for any entity which will accept access tokens and grant access to resources or perform actions. Connect is a resource server when you use access tokens to make requests on a user's behalf. |
| refresh token | A token which can be used to obtain a fresh access token when the previous one has expired. |
| token endpoint | The HTTP endpoint at which the authorization server grants tokens. For Connect, this is /oidc/token. |
 References
Content in this tutorial is adapted from OpenID.
References
Content in this tutorial is adapted from OpenID.
OpenID® copyright (c) 2013 The OpenID Foundation
Related topics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Use Your Own Security Certificate
Last updated: 23 May 2024